| [ BNC query result | File and speaker information | Sort | Thin | Subcorpus | Distribution | Collocations | Tag sequence search | Delete hits | Save current hits | Download | Main page options ] |
Performing a Subcorpus query |
A Subcorpus query is rather like a Standard query, but limited to a subsection of the corpus. To query a subcorpus of the BNC, you must first have already:
Subcorpus query steps |
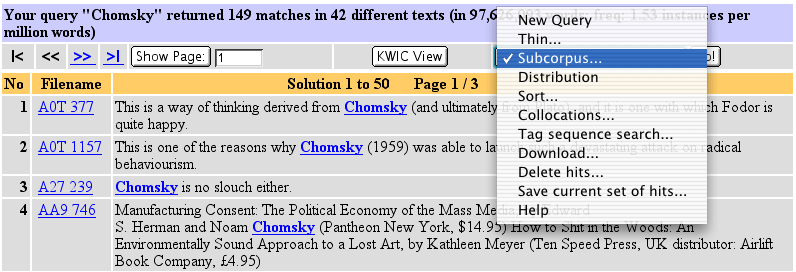
Step 1: Perform a Standard query. The following screenshot shows the result for a standard query on the word "Chomsky" (with the drop-down menu on the right opened).

As the above picture shows, there are 149 matches in 42 different texts. But how many of these references to Chomsky are in academic texts or journals (as opposed to newspaper articles reporting Chomsky's latest political activities, for example)? Suppose we have earlier already created a subcorpus called "academic" consisting of all academic texts in the BNC. We now need to restrict our results to this subcorpus.
Step 2: Select the "Subcorpus" option from the drop-down menu, then hit "Go!". You will see a screen like the following:
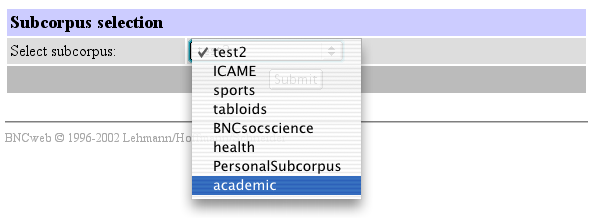
Select the subcorpus you want to restrict your results by (in this case, "academic"), then hit "Submit".
You will now see the following screen:
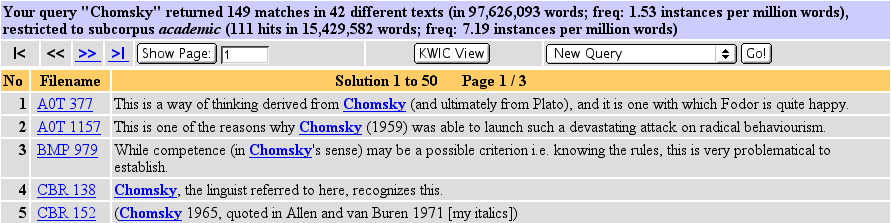
Note that the initial results have now been filtered to exclude non-academic texts. The results show that 111 hits (out of the original 149 for the whole BNC) were from the "academic" subcorpus. In order to facilitate comparison between various subcorpora, relative frequencies are always indicated for both your initial query result and the filtered set.
Notes |
| [ BNC query result | File and speaker information | Sort | Thin | Subcorpus | Distribution | Collocations | Tag sequence search | Delete hits | Save current hits | Download | Main page options ] |